Proc. of
Contribution of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase to the Carbon Economy of cv. Fuerte Avocado Fruit - Categorization of Photosynthesis and Effects of Simulated Salinity, CO2 Shock and CA-Storage
Brian A. Notton
Department of Agricultural Sciences,
Michael M. Blanke
Institut für Obstbau und Gemüsebau,
Abstract. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC, orthophosphate:oxaloacetate carboxylase [phosphorylating], EC
4.1.1.31) was extracted and partially purified from the mesocarp
of pre-climacteric avocado cv. Fuerte
(Persea
Abbreviations: dithiothreitol (DTT); malate dehydrogenase (MDH); 3-[N-morpholino] propanesulfonic acid (MOPS); nicotinamide adenosine dinucleotide [reduced form] (NADH); oxaloacetic acid (OAA); Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP); N-tris[hydroxymethyl]-methyl glycine (Tricine).
Avocado (Persea
Materials and Methods
Fruit. Pre-climacteric avocado (Persea
Enzyme extraction. Extraction buffer was used appropriate to the particular experiments, either 200 mM Tricine/NaOH (pH 7.8) or 200 mM MOPS/NaOH, (pH 7.0), containing 3 mM DTT, 2.5 mM MgSO4 and, except for the bicarbonate kinetics experiments, 5 mM NaHCO3- All extracts were prepared at 4C. The mesocarp was diced and the tissue ground with a cold pestle and mortar in appropriate buffer in a 3:1 ratio together with clean sand and 2% (w/v) PVP to respectively aid extraction and to prevent browning of the solution. The homogenate was filtered through muslin and the filtrate centrifuged at 20,000 g for 30 min. The aqueous phase was removed from debris and floating oils using a hypodermic needle and syringe. The clear solution was made 65% saturated with respect to (NH4)2SO4 by addition of the appropriate quantity of a cold, saturated solution of (NH4)2SO4 previously adjusted to pH 7.8 with NH4OH. After 45 min stirring, the mixture was centrifuged at 20,000 g for 30 min and the resultant pellet dissolved in 10% of the initial volume of the extracting buffer, using 50 mM Tricine (pH 7.8) or 50 mM MOPS buffer (pH 7.0) containing 1 mM DTT, 2.5 mM MgSO4, 5% glycerol and, as appropriate, 5 mM NaHCO3.
Enzyme assays. Activity of PEPC was determined spectrophotometrically
as previously described (Blanke et al., 1986)
at 340 nm by coupling the reaction to the oxidation of NADH in the presence of
MDH. One unit of PEPC activity is expressed as OD change at 340 nm of 1.0 per
minute per gram tissue. The standard assay medium contained enzyme, 10 units of
MDH, and 0.1 mM NADH, 2.5 mM
MgSO4 and 5 mM NaHCO3 in a
total volume of 2.95 ml 50 mM
Tricine buffer (pH 7.8), at 27C. The reaction was
started by the addition of 50 µL of PEP at 2.2 mM
final concentration. The assay mixture, in the spectrophotometer cuvette, was rapidly mixed in situ using a mini
magnetic bar and an electronic stirrer type 200 (Rank Brothers, Cambridge
CB59DA,
Enzyme kinetics. Values for Kpp, and Vmax were calculated as previously described (Blanke et al., 1987) using a kinetics computer programme (Transcribe,
Simulated CO2 shock. CA storage and salinity. CO2shock, CA storage and salinity were simulated by exposing avocado fruit extracts to the equivalent CO2/HCO3 (Table 1) or NaCI concentration during the assay for PEPC at 27C.
Measurement of ambient CO2
. The ambient CO2 concentration during the
CO2/HCO3 kinetics experiments was monitored using a
digital portable infrared gas analyzer type LCA 2 (ADC, The Analytical
Development
Fruit porometry. Respiration of avocado fruit was measured by a portable porometer type LCA 3 from ADC. The fruit cuvette consisted of two transparent hemispheres (Blanke and ADC, 1992). Flow rates into the fruit cuvette and into the LCA 3 were controlled by the two mass flowmeters of the LCA 3. Fruit temperature was recorded by a thermistor on a flying lead pushed into the mesocarp.
Results and Discussion
Role of PEPC in fruit. The enzyme PEPC combines HCO3 from intracellular CO2 with PEP to produce oxaloacetate (OAA), which in turn is converted to malate (Fig. 1). The substrate PEP originates from metabolic conversion of starch or sugars. The properties of the enzyme PEPC have been widely used to examine the photosynthesis of a plant organ such as fruit, leaf or root (Blanke and Lenz, 1989).
Carbon conservation by
PEPC in pre-climacteric avocado fruit. The maximal activity of CO2 refixation
potential of PEPC in the mesocarp of pre-climacteric
'Fuerte' avocado fruit was 106 /µmol CO2/fruit/h,
thereby exceeding the respiratory CO2 efflux from the fruit of 50 µmol
CO2/fruit/h by ca. two-fold (Fig. 2). However, the CO2 refixation potential included any enzyme loss during the
extraction and was determined under optimum conditions for maximal enzyme
activity, i.e. saturating concentrations of cofactors and substrates at pH 7.8.
It may be assumed that the enzyme activity or CO2 refixation potential is significantly lower in the fruit
than in the test tube. Metabolic regulation of PEPC by supply of substrate and cofactors, makes it more likely that the enzyme refixes CO2 in quantities which are of the same
order of magnitude as the CO2 lost from the fruit through the peel.
Thus a substantial amount of carbon (ca. 50%) was conserved in pre-climacteric
avocado fruit by the activity of PEPC and this contributed to the carbon
economy of the fruit.
Effects of salinity on avocado fruit
PEPC. The vast water requirement of
the fully grown avocado tree can often only be met by irrigation, e.g. in
Chloride inhibited activity of PEPC from pre-climacteric 'Fuerte' avocado fruit in a concentration-dependent manner at pH 7.8 (Fig. 3); this effect on PEPC activity had been observed with PEPCs from C3 and C4. photosynthetic leaves (Ting and Osmond, 1973). Chloride at a concentration of 180 mM NaCI in the PEPC assay decreased PEPC activity by 30% at saturating (2.2 mM) PEP concentration. We have shown (Blanke and Notton, 1991) that the degree of inhibition is dependent on the concentration of the substrate PEP, e.g. PEPC activity was inhibited 50% by 180 mM NaCI when the PEP was at a subsaturating concentration of 0.5 mM. The concentration of PEP occurring in fruit is likely to be subsaturating with respect to PEPC, thereby enhancing chloride inhibition effects. Chloride at 180 mM caused an almost three-fold increase in apparent Km (PEP) from 80 µM to 212 µM PEP, accompanied by a 14% decrease in Vmax. This effect on apparent Km and Vmax resembles that reported for the chloride inhibition of PEPC from C3 photosynthetic leaves (Ting and Osmond, 1973) which was thought to be due to competition of chloride with PEP binding to PEPC.
Effects of CO2 shock and CA storage on
intercellular CO2; and cellular HCO3 levels. Mature, unripe, refrigerated avocado fruits are
shipped from
Effects of CO2 shock and CA storage on PEPC in pre-climacteric avocado fruits. The enzyme PEPC is located in the cytosol in the mesocarp of the avocado fruit and has two substrates, HCO3/CO2 and PEP. Effects of CO2 shock and CA storage were simulated by assaying for PEPC activity under the equivalent HCO3 concentrations at pH 7 (Table 1). The Michaelis-Menton constant (Km), i.e. the substrate concentration which gives half maximum enzyme activity, of PEPC was calculated to be 14 µM HCO3, taking into account 63 µM HCO3 from the 450 ppm ambient CO2 in our laboratory. Maximum PEPC activity was observed between 0.2 and 125 mM HCO3. These bicarbonate concentrations are equivalent to 0.14% and 87% CO2 in the intercellular space which indicates that the CO2 refixation by PEPC appears not inhibited by the high intercellular CO2 concentration in the avocado fruit under CO2 shock or in CA storage.
Interaction between salt concentration and the two substrates of PEPC. At a constant salt concentration adjusted to 1 50 mM (buffer containing endogenous HCO3 plus added HCO3), no CO2/HCO3 inhibition was observed at pH 7.0 and concentrations up to 125 mM HCO3 (Fig. 4). Under saturating PEP concentrations, PEPC activity showed a non-competitive relationship between both substrates, HCO3 and PEP, a result similar to that found for apple fruit (Blanke et al., 1987). This was as expected given the proposed CO2 concentrating mechanism of PEPC in fruit (Blanke, 1992).
Conclusions
Much of the fascination in studies with avocado fruit lies in (a) attempting its photosynthetic classification, (b) in the potential to contribute to its carbon economy and (c) to explain differences in response of cultivars to CO2 under CO2 shock and in CA storage. Further research is needed to identify the role of PEPC in the carbon metabolism of avocado fruit and to investigate effects of CO2 shock or CA storage on respiration and fruit metabolism.
We gratefully acknowledge travel grant 477/ 157/91 and grant Bl 263/2/3 from DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft).
Literature cited
Blanke,
M.M. 1992. Photosynthesis of avocado fruit. Proc. of
Blanke, M.M. and ADC. 1992. Use of the ADC LCA 3 in avocado fruit physiology. Proc. of
Blanke, M.M., and F. Lenz. 1989. Fruit photosynthesis. Plant, Cell and Environment 12: 31-46.
Blanke, M.M., and B.A. Notton. 1991. Physiological significance of photosynthetic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in avocado fruit. J. Plant Physiol. 137: 553-558.
Blanke, M.M., D.P. Hucklesby, B.A. Notton, and F. Lenz. 1987. Utilization of bicarbonate by apple fruit phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Phytochem. 26:2475-2476.
Blanke, M.M., B.A. Notton, and D.P. Hucklesby. 1986. Physical and kinetic properties of photosynthetic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in developing apple fruit. Phytochem. 25:601- 606.
Ting, I.P., and C.B. Osmond. 1973. Photosynthetic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylases. Plant Physiol. 51:439-447.
|
Table 1. Effect of postharvest
treatment of 'Fuerte' avocado fruit on equilibria between intercellular CO2 concentration
and solute bicarbonate (HCO3) at pH 7 in the cytosol,
compared to the CO2/HCO3 range for maximal PEPC
activity in the mesocarp. z |
||
|
Treatment |
CO2concentration y (%) |
HCO3- concentration (mM) |
|
Harvest |
1-3 |
1.4-4.2 |
|
CO2 shock |
20 |
28 |
|
CO2 shock |
25 |
35 |
|
CO2 shock |
30 |
42 |
|
CA storage |
10 |
14 |
|
Maximal PEPC
activity ranges |
||
|
From |
0.14% |
0.2 mM |
|
To |
87% |
125 mM |
|
z Data calculated from Henderson-Hasselbach equation. y The ambient CO2 concentration is ca. 0.034% CO2. |
||
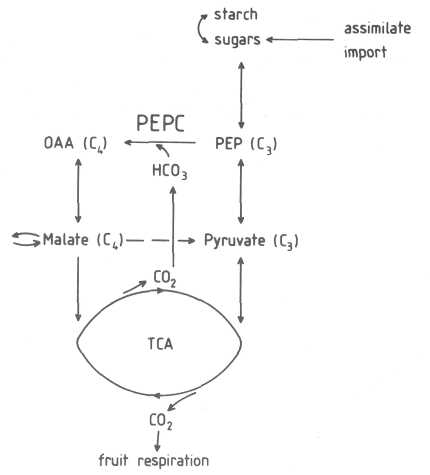
Fig. 1. Schematic of the biochemical reactions involved in respiration and CO2 refixation. Avocado fruit tissue respires assimilates in the tricarboxylic (TCA) cycle, thereby producing CO2. This CO2 partly accumulates in the intercellular spaces, is partly refixed as soluble bicarbonate (HCO3) by the action of the enzyme PEPC or is respired through the fruit peel.
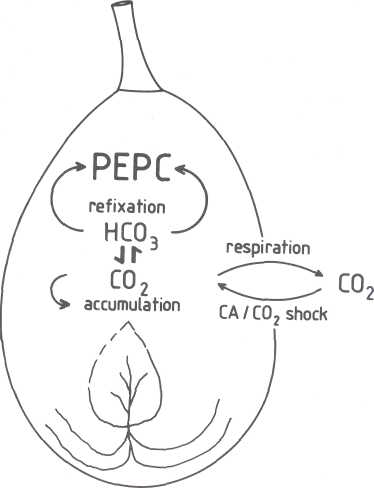
Fig. 2. Schematic of respiration and CO2 refixation in avocado fruit. Fruit tissue respires CO2. The enzyme PEPC refixes CO2 in the soluble form of bicarbonate. The CO2 which is not refixed, accumulates within the fruit or is respired through the peel. In CA storage or under CO2 shock, ambient CO2 penetrates the fruit.
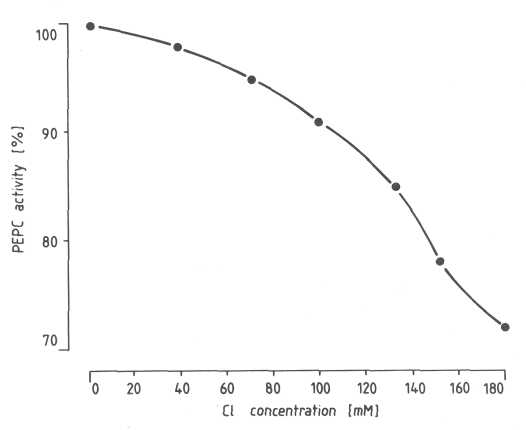
Fig. 3. Effect of salinity on PEPC from 'Fuerte' avocado fruit. PEPC was assayed at pH 7.8 after addition of 0 to 180 mM chloride at saturating (2.2 mM) PEP and (5 mM) HCO3 concentration.
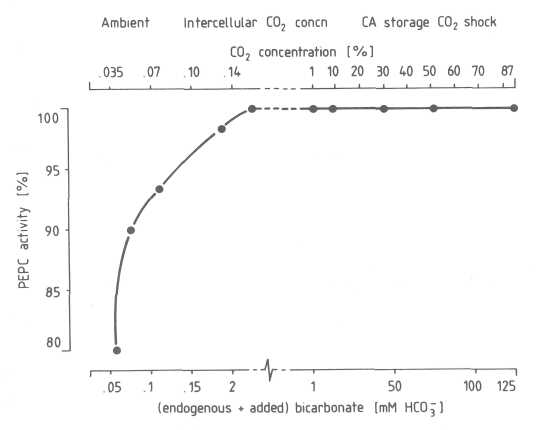
Fig. 4. Effect of CO2/HCO3 on PEPC from pre-climacteric avocado fruit. PEPC was assayed under saturating (2.2 mM) PEP concentration at pH 7.0 in the presence of up to 125 mM HCO3 and taking into account the endogenous ambient CO2 .